Building a Successful MVP
Almost every startup begins with a game-changing idea that should revolutionize the way the world functions. However, many passionate entrepreneurs invest time and energy into building a polished, perfect product only to discover that it solves a problem nobody cares about.
So what went wrong? Simple. The majority of those great ideas are built on assumptions nobody has tested. So ask yourself a question – how do you know your future project is something customers are looking for? That’s where MVP comes into play.
Building an MVP for startups is a great way to investigate the market with less cost and time loss compared to implementing a full-fledged solution. And our team will gladly assist you in your startup journey.
What is a Minimum Viable Product (MVP)?
Defining MVP is a bit confusing because there are many definitions available. Basically, it means building a product that contains enough features to satisfy early customers and provide feedback for future product development. This ensures that the features are tailored to the specific needs of users and can enhance a product.
Benefits of Building an MVP
MVPs are designed to quickly launch products based on established ideas within a small budget. This helps businesses to identify the features that users find most useful and those that can be cut from the product. What’s more, an MVP can also help measure market potential and give businesses access to invaluable user data that can inform their product development strategy over time.
Stats Emphasizing the Need for MVPs
- Poor financial planning and cash flow problems account for 44% of startup failures
- Properly scaling startups grow much faster than prematurely scaling startups.
With these stats, it is clear that starting the new product development process with an MVP has many benefits. Startup companies build a Minimum Viable Product for a number of reasons:
- Establishing an initial model that offers clear visual references and serves as a starting point for discussions
- Testing the model with real users and sharing it with a few prospects
- Building a fully-fledged product after months of development and refinement is a significant and motivating step toward product advancement
MVP development can be split into phases:
- Business and Marketing: Launching an MVP allows businesses to identify the best marketing approaches and advertising platforms for the advancement of their product.
- Proof of Concept: Building an MVP will give the business crucial technical insight so they are able to build a premium product that stands out from the crowd.
How to Build a Minimum Viable Product
The main goal of an MVP is to develop a working product that provides immediate value while minimizing costs. Starting with an MVP will help you better understand your end user and the market you want to enter. In some cases, an MVP can also be used to show stakeholders what the business has to offer. Therefore, an MVP is an excellent way to prove your product’s merit and secure future funding.
Below we outline the steps you should take to create a successful MVP and discuss in detail what occurs at each stage.
- Identify the Problem Your Product Should Solve
To ensure the success of your Minimum Viable Product, it’s important to understand your users’ needs and how your product will meet them. This is the stage where you should get your potential target audience’s initial feedback. Ask yourself the following questions:
- Does my product make any use?
- How can it help my customers?
- Why would my customers want to use my product?
By answering these questions, you’ll be able to develop a minimum viable product with a clear purpose.
- Research the Market
Now that you have chosen your product idea, let’s get to know your competitors. It’s important to remember that lots of promising startups failed only because they were tested in a limited environment. Since the market is already saturated with similar products, you should do thorough market research to make sure your product will have the edge. Competitor analysis involves understanding the strengths and weaknesses of your competitors, their pricing strategies, their product offerings, and other factors that can give you an advantage in the market. It also involves understanding the current trends in the market and the needs of your target audience.
- Create Your Unique Value Proposition
Once you have conducted market research and considered the users’ problems, you can select the features most valuable to the customers for the minimum viable product. As we build the smallest version of our product, we must identify the core features we can’t live without, and the ‘nice to have’ features that will help our product scale.
It’s a good thing there are so many different frameworks available to help you prioritize your feature list, including Value Proposition Canvas – a tool that can help ensure that there is a fit between the product and market:
There are three key points: Jobs-to-be-done, Pains, and Gains. To define how to make an MVP product that meets the needs of the customers, you need to fill out each component.
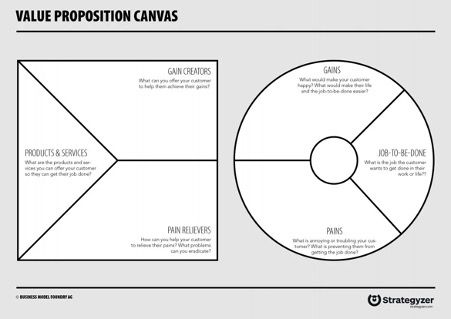
Source: Strategyzer.com
Below is an example of Tesla VPC finding the best fit between the product and the market.
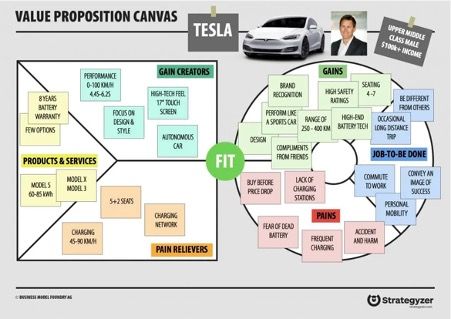
Source: Designabetterbusiness.com
Using this example, you can place the most important features in the ‘must-have’ column and the less significant ones into the ‘additional’ column. Organize the features in columns so that the most important one appears at the top.
Such ranking will help you prioritize the customer’s needs and create a blueprint for how to best meet those needs. This will ensure a seamless fit between the customer’s needs and the product offered.
- Prototype Your Idea
Having done the market research, and considering all the strengths and weaknesses of your potential competitors, you need to substantiate your idea before moving onto the MVP development stage. The best way to make an MVP is to make a prototype first.
Prototyping is one of the principal stages of product development with СyberCraft. Prototypes help you visualize the design and functionality, validate the UI & UX, and get early feedback so that you can improve the MVP accordingly. Below you can see an example of a prototype that our team created for PickMe, a successful photo contest application.
- Build, Measure, Learn
A process is involved in everything: first, define the scope of work, and then move the product towards development. Once the product is released, it’s important to keep testing it. Continuous testing and monitoring of the product should be done to ensure that it still meets customer needs. Testing can be done in different ways, for example through user testing, surveys, and other feedback metrics. Based on these metrics, the company can determine how competitive its products are in the market.

Measuring Success After Building an MVP
Your product’s financial success is measured by the number of paid customers and the revenue you generate each month. These metrics are the most informative ones, although not actionable enough.
Here are some things you can do to make sure your MVP is performing well:
- Run an NPS survey
An NPS survey, or net promoter score, provides the most convenient way to gather data about how satisfied users are with your products or services. It will let you know if the users are loyal to your product and if they recommend it to others based on their satisfaction level.
- Monitor the number of active users
Tracking your active users is the best way to make sure your product is successful. As you monitor it, you will be able to assess a still more important metric – engagement with the product.
- Measure your product’s lifetime
Now that you know the number of active users you have, it’s important to check how long they stay on your platform, as this has a direct impact on your monthly income. A good way to measure your product lifetime is to come up with an engagement model so your users can score your product. In addition to measuring the success of your product, engagement scores also help you plan for the future. It will help you identify future research participants and potential power users.
Building an MVP: Top Mistakes to Avoid
Building an MVP, it is essential to plan for potential risks before they can become major issues. Here are the most common mistakes to avoid when launching your first product version:
- Striving for excellence
MVPs are limited products with limited functionality that help the user evaluate essential features and functions. Don’t overcomplicate the test-version development, as this will only slow it down.
- Failing to collect feedback
The users must have a basic understanding of the product in order to be able to use it effectively. No amount of design or performance will save a product if customers do not find it interesting. Collect feedback, enhance users’ experience and make sure every customer has their say.
- Excess saving
It doesn’t make sense to spend too much time and money on unnecessary functionality. But does it mean you have to save on everything? Of course not. Key functions should be of top quality, otherwise, your product will die at the very beginning.
Wrap Up
Though it looks huge, taking that first step is an essential part of any successful venture, so investing effort into getting your MVP right is key. This lets you get feedback from real users, get validation from stakeholders, and prove your idea works. Now you have a solid foundation for developing your MVP and can begin to move forward with your project with confidence. Having built products for startups for more than 10 years, we understand the importance of starting small and building a great product. Get in touch with us if you are looking for a product partner to assist you with MVP development. Let’s start a new journey together!